‘BeyondCorp’ was Google’s initiative of 2010 that paved the way for secure access to corporate resources from any location or device without a VPN. This was the first instance of an implementation of the zero trust approach that aimed at enhancing security with a focus on identity and context rather than relying solely on perimeter-based defenses.
Zero trust model: a paradigm shift in cybersecurity
The need for continuous authentication and authorization led to a ‘never trust, always verify’ principle that became the basis of a new model proposed by Forrester Research analyst John Kindervag in 2014. ” In a report titled “No more chewy centers: introducing cybersecurity zero trust,” John Kindervag mentioned that zero trust assumes no one, whether inside or outside the network, can be trusted without verification.
In today’s world, cybersecurity threats are more complex and sophisticated than ever before. Traditional security models are no longer sufficient to protect sensitive data. Organizations need to adopt new approaches to ensure that their data is secure.
Zero trust is one such approach that offers a more effective way to protect sensitive data. Let’s find out why zero trust is a good approach toward cybersecurity.
The zero trust security model coils around the idea of every user, device, or application being a potential threat until proven otherwise. This approach has gained popularity in recent years due to the increase in cyberattacks and the need for more comprehensive security strategies.
Do we really need a zero trust model to protect our organizations?
A substantial number of organizations around 41%, participating in a global survey expressed their commitment to implementing a cybersecurity zero trust strategy, signifying a growing recognition of its benefits and an early phase of adoption.
Implementing a zero trust approach is, undoubtedly, one of the most effective ways to protect our organizations against cyber threats, but whether it is necessary for your specific organization depends on a variety of factors.
If your organization deals with sensitive data, such as financial or personal information, or if you have valuable intellectual property that needs to be protected, then implementing a zero trust model is highly recommended. Zero trust can help prevent data breaches, reduce the risk of insider threats, and provide better control over user access to sensitive resources.
However, if your organization doesn’t handle sensitive information, and you have a small, well-defined network perimeter, you may not need to implement a cybersecurity zero trust model. In this case, traditional security measures such as firewalls, antivirus software, and intrusion detection systems may be sufficient.
Ultimately, the decision to adopt zero trust security services should be based on a comprehensive risk assessment and an understanding of your organization’s specific security needs and resources.
How does zero trust security work?
Zero Trust involves implementing a set of security policies and controls to authenticate and authorize every access request to resources, regardless of the user’s location or the device they’re using. This includes implementing multifactor authentication, role-based access controls, and continuous network traffic monitoring. To achieve this, organizations need to adopt a holistic approach that includes people, processes, and technology.
With the rise of remote work and cloud computing, the traditional perimeter-based security approach is no longer effective. Zero trust offers a more effective way to protect sensitive data by limiting access to only authorized users and devices. By adopting this approach, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of data breaches and protect their sensitive information from unauthorized access.
Moreover, zero trust can comply with organizations’ help with data protection regulations such as the GDPR and the upcoming ‘Personal Data Protection Bill’ in India. By implementing zero trust, organizations can demonstrate their commitment to protecting the privacy of their customers and employees.
How can the zero trust model be a game changer?
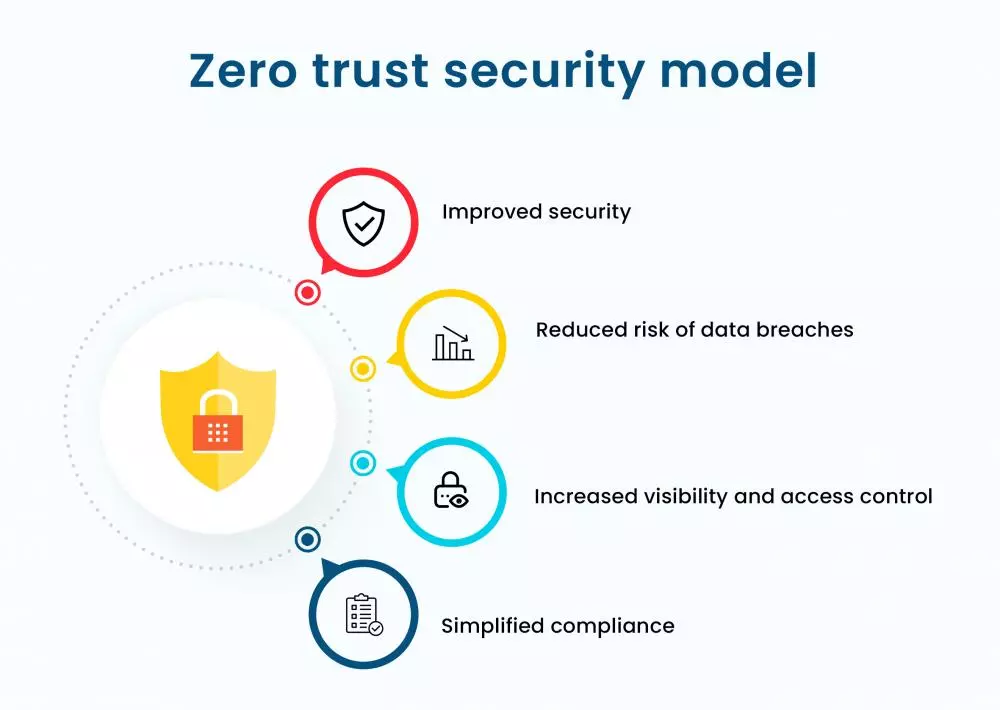
Zero trust security model provides
- Improved security
- Reduced risk of data breaches
- Increased visibility and control over network access
- Simplified compliance with industry regulations
As organizations rely on digital technologies, the need for robust cybersecurity measures has become more critical than ever before. The zero trust model provides a comprehensive and effective approach to cybersecurity, offering enhanced security, reduced risk, improved compliance, and increased visibility. Implementing this model may require significant effort, but it’s a worthwhile investment in protecting sensitive business-critical data and safeguarding against cyber threats.
We at InfoVision help our clients to reduce risks (ransomware, supply chain attacks, insider threats) by providing consideration services like SOC (Security Operation Center), multifactor authentication (MFA), identity management, access management, identity governance, SSO & federation, and privileged access.
Why incorporate the zero trust model in your business?
If you go with the stats, between 2021 and 2022, there was a 2.6% increase in the average cost of a data breach, with the figure rising from $4.24 million to $4.35 million. And implementing the best Zero Trust solutions or approach can result in substantial cost savings, reducing the financial impact of a data breach by approximately $1 million.
Zero Trust provides a more effective way to protect sensitive data in today’s digital world. By adopting a zero trust approach, organizations can limit access to only authorized users and devices, significantly reducing the risk of data breaches.
This zero trust access management also helps organizations comply with data protection regulations, ensuring that they protect the privacy of their customers and employees. The need for zero trust is more critical than ever, and organizations should consider adopting this approach to ensure the security of their data.
Keeping up with zero trust trends
Endpoint security
Organizations are increasingly embracing Zero Trust principles to enhance endpoint security. This involves continuous monitoring of device health and strict access control enforcement. The objective is to eradicate implicit trust, ensuring that all access to assets and users is rigorously verified, thereby elevating security measures.
Cloud-first zero trust platforms
Cloud-first Zero Trust platforms are rapidly gaining popularity due to their inherent benefits. They are known for being cost-effective and scalable, offering clientless capabilities as an alternative to traditional endpoint agents. This innovative approach is making waves in the security landscape.
Increasing adoption of zero trust
Currently, a substantial 83% of security professionals consider Zero Trust a vital part of their security strategies. Remarkably, 80% of them intend to implement Zero Trust in 2022. This widespread commitment reflects a growing recognition of its crucial role in enhancing overall security posture.
Zero trust in different sectors
Sectors like insurance, financial services, and manufacturing now recognize Zero Trust as paramount for enhancing visibility and control over their endpoints. They are actively integrating Zero Trust principles into their cybersecurity strategies to bolster their defenses, acknowledging the potential benefits.
Zero trust as a cybersecurity concept
Zero Trust stands as a foundational cybersecurity concept aiming to eradicate implicit trust within security frameworks. Its core tenets involve continuous access verification and the enforcement of the principle of least privilege. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has provided comprehensive guidelines for the design and deployment of Zero Trust architectures.
Now pick the right cybersecurity partner for your business with the help of our MDR-made simple whitepaper. Download here: MDR made simple: picking the right cybersecurity partner for your business (infovision.com)
Integration with DevSecOps
Incorporating security practices into the development pipeline has become a crucial strategy for organizations. This proactive approach ensures that security is an integral part of application and service development right from the start.
Zero trust network access (ZTNA)
The increasing prominence of Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA), often referred to as “Software-Defined Perimeters,” is remarkable. ZTNA solutions empower organizations to finely manage user and device access to specific resources, regardless of their physical location. This capability plays a significant role in reducing potential vulnerabilities and boosting overall security.
In the realm of cybersecurity innovation, our solution, Invisinet is making its mark. Built upon the intellectual property of Blackridge, Invisinet serves as the gateway to where Zero Trust truly begins.
Invisinet’s network and cloud security solution called Transport Access Control (TAC) enables efficient cyber defense in IIoT, smart edge, and cloud settings. TAC stops unauthorized access to IT/OT resources.
Invisinet First Packet Authentication is a crucial feature of TAC, which inserts a cryptographically generated, single-use identity token on each side of a TCP/IP session without affecting TCP compatibility. When TAC receives the connection request, it extracts and authenticates the identity token, and applies a security policy – forward, redirect, or discard – based on the TAC identity.
So, TAC’s identity-based protection kicks in as soon as it can, making sure that any unauthorized or unknown traffic is barred from your network, enhancing security, and lowering risk.
To learn more about First packet authentication by Invisinet and the zero trust cybersecurity model, contact InfoVision’s expert team at info@infovision.com.