SAP sits at the core of most of the enterprises. Modern organizations depend on SAP to synchronize their mission-critical operations across finance, supply chain, procurement, HR, billing, manufacturing, customer operations and a complex ecosystem of integrated applications. The impact of any disruption to this ecosystem, whether stemming from outages, cyber incidents, infrastructure failures, or natural disasters, extends beyond IT, resulting in measurable business disruption and financial disaster.
This reality mandates that leaders make a serious note of building ‘resilience’ into this tightly integrated ecosystem because DR, particularly in the context of SAP, is no longer about bouncing back from an outage. It is about synchronizing recovery with business continuity.
What is SAP disaster recovery and why it matters?
SAP disaster recovery is a structured approach that combines processes, technology, and architecture to restore SAP systems when disruptions occur. Because SAP runs real-time, business-critical transactions, even brief downtime can ripple across the enterprise impacting revenue, regulatory compliance, customer experience, and employee productivity.
A well-designed disaster recovery strategy safeguards the reliability, availability, and integrity of SAP workloads, ensuring business continuity when it matters most.
Key Objectives of SAP Disaster Recovery
SAP disaster recovery is not just a technical safeguard; it is a business continuity imperative. Its objectives include:
- Minimizing operational disruption and downtime
- Restoring SAP production systems quickly and reliably
- Protecting data integrity across all modules and interfaces
- Maintaining compliance with organizational SLAs and legal requirements
To achieve these objectives, SAP DR strategies are built around clearly defined response workflows that map directly to the nature of the disruption. Common SAP downtime scenarios and their corresponding DR actions include:
- System failure: Automated failover to standby SAP systems to restore application availability.
- Hardware or power outage: Controlled switchover to a secondary data center to maintain business operations.
- Cyberattack: Activation of secured backups and immutable snapshots to recover clean system states.
- Network disruptions: Traffic redirection to an alternate region to sustain user access and transaction flow.
Together, these scenario-driven workflows ensure SAP environments remain resilient, recoverable, and aligned with business continuity commitments, even in high-impact failure situations.
Architecture That Assumes Disruption Will Happen
Resilient SAP landscapes are designed with the assumption that failures are inevitable. The differentiator is not whether disruption occurs, but how quickly and cleanly the organization responds.
Modern SAP environments leverage real-time data replication, automated failover, and disciplined backup strategies to ensure transactional consistency across primary and secondary systems. The focus is on controlled recovery.
Equally critical is the ability to return operations back to the primary environment once stability is restored, without introducing additional risk or downtime.
Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity Must Move Together
A common failure pattern across enterprises is treating Disaster Recovery (DR) and Business Continuity (BC) as parallel but disconnected initiatives. In reality, one enables the other.
Disaster Recovery restores SAP systems. Business Continuity ensures the organization can operate while restoration is underway and immediately after systems come back online. When these plans are aligned, recovery workflows support enterprise-wide response protocols, clear communication flows, and visibility and control during disruption.
This alignment is what separates technical recovery from business resilience.
- DR restores systems; BCP ensures the business continues to operate
- DR workflows support organization-wide recovery procedures
- RTO (Recovery Time Objective)/RPO (Recovery Point Objective) targets map directly to operational continuity needs
Core Elements of an Effective SAP Disaster Recovery Plan
An effective SAP DR strategy is built on a combination of clearly defined recovery objectives, resilient technical architecture, and well-documented operational processes. Together, these elements ensure that recovery is not improvised during a crisis but executed with precision and predictability.
1. Defining RTO and RPO
At the foundation of any SAP disaster recovery plan are clearly articulated recovery objectives that align IT capabilities with business tolerance for disruption.
- Recovery Time Objective (RTO) defines the maximum acceptable duration of SAP downtime after a disruption.
- Recovery Point Objective (RPO) defines the maximum acceptable window of data loss, measured in time.
Establishing realistic RTOs and RPOs ensures that disaster recovery investments are proportionate to business risk and operational criticality.
2. Replication approaches
Replication plays a central role in meeting defined RTO and RPO targets. The choice of replication strategy depends on distance, performance requirements, and data loss tolerance.
- Synchronous replication enables real-time write operations across primary and secondary sites, resulting in near-zero data loss.
- Asynchronous replication offers lower latency and is more suitable for long-distance disaster recovery sites.
Selecting the right replication model is a balance between performance, resilience, and business risk appetite.
3. Documentation of the disaster recovery framework
Even the most robust technical setup can fail without clear documentation and execution clarity. A comprehensive DR framework should include:
- Detailed architecture diagrams that illustrate system dependencies and recovery paths.
- Clearly defined backup, restore, and replication schedules.
- Step-by-step recovery runbooks and escalation plans to guide teams during high-pressure scenarios.
- Established communication workflows to ensure stakeholders are informed and coordinated throughout the recovery process.
4. High availability vs. disaster recovery
While often discussed together, high availability and disaster recovery serve distinct but complementary purposes within SAP landscapes.
- High Availability (HA) focuses on ensuring continuity by eliminating single points of failure within the same site, using clustering and redundancy to prevent localized outages.
- Disaster Recovery (DR) focuses on recoverability, enabling SAP systems to be restored in the event of large-scale failures by activating a geographically separate environment.
In essence, HA minimizes disruption, while DR ensures the business can recover when disruption exceeds the limits of local resilience.
Testing Is Where Most Strategies Break Down
A Disaster Recovery plan that exists only on paper is not a plan. It is an assumption.
Regular DR drills expose the gaps that architecture diagrams may not show, such as, hidden integration dependencies, manual steps that slow recovery, performance or data consistency issues that surface only under load.
Organizations that test rigorously treat each drill as a learning cycle.

Approaches for SAP Disaster Recovery, Testing and Metrics
SAP disaster recovery approaches vary based on deployment models, risk tolerance, and business criticality. Whether operating in the cloud, on premises, or across hybrid environments, organizations must align recovery architecture with operational objectives, testing rigor, and measurable outcomes.
Cloud-native and On-prem DR Approaches
Cloud-native DR Options (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud) | On-prem Backup and Restore Stategy |
|---|---|
Automated provisioning of DR systems | Full/incremental/differential backups |
Region-to-region replication | Encrypted storage |
High-speed storage for backups | Automated verification and restore tests |
Elastic scale-up during fallover | Support for point-in-time recovery |
Benefits of multi-region replication
Multi-region replication plays a critical role in strengthening SAP resilience, particularly for globally distributed enterprises. Key benefits include:
- Greater resilience against large-scale regional outages
- Reduced recovery time and recovery point objectives
- Improved compliance with data residency and regulatory requirements
By decoupling recovery from a single geography, organizations can better absorb systemic disruptions.
Challenges in hybrid or on-premises deployments
While hybrid and on-premises DR models provide flexibility, they also introduce complexity that must be actively managed:
- Complex network configurations and identity management across environments
- Mixed replication and backup tooling, increasing operational overhead
- Difficulty maintaining consistent SLAs across disparate platforms
Without careful design and governance, these challenges can erode recovery predictability.
Testing and maintaining SAP disaster recovery
A disaster recovery strategy is only as strong as its testing discipline. Regular DR drills are essential to validate both technical readiness and organizational coordination.
Effective testing programs typically include:
- Table-top simulations combined with full-scale DR drills
- Verification of achieved RTO and RPO targets
- Data consistency and integrity checks post-recovery
- Validation of automated versus manual recovery steps
- Performance benchmarking after failover
Monitoring tools commonly used
Continuous monitoring provides visibility into SAP health, replication status, and recovery readiness. Commonly used tools include:
- SAP HANA Cockpit for database-level monitoring and performance insights
- SAP Landscape Management (LaMa) for system orchestration and lifecycle management
- Cloud-native monitoring tools such as Amazon CloudWatch and Azure Monitor for infrastructure and service-level observability
These tools support proactive detection and faster response during failure scenarios.
Disaster recovery testing metrics
To assess the effectiveness of SAP disaster recovery, organizations should track measurable, outcome-driven metrics, including:
- Achieved RTO and RPO during DR drills
- Time required to verify data consistency
- Number of manual steps involved in recovery execution
- System stability and performance benchmarks following failover
Metrics convert DR readiness into quantifiable assurance.
Common pitfalls to avoid
Despite significant investment, SAP disaster recovery initiatives often fall short due to avoidable gaps:
- Relying solely on backups without validating end-to-end DR workflows
- Outdated or incomplete documentation
- Lack of coordination across infrastructure, application, and business teams
- Underestimating dependencies across integrated SAP and non-SAP applications
- Infrequent or superficial DR testing
Avoiding these pitfalls is essential to ensuring that disaster recovery performs as expected when disruption occurs.
Checklist for a Resilient SAP Disaster Recovery Framework
Readiness is built through disciplined preparation and rigorous validation. A resilient SAP Disaster Recovery framework balances both.
Pre-Disaster Preparation
- Updated SAP DR architecture and recovery runbooks
- Verified backup and replication health across systems
- DR infrastructure provisioned and tested
- Clear communication and escalation plans
Post-Recovery Validation
- End-to-end system and data integrity checks
- Application and integration testing across the SAP landscape
- Documentation of recovery outcomes and lessons learned
Continuous Improvement Is Non-Negotiable
- SAP Disaster Recovery is not a one-time implementation. It is an evolving capability that must mature alongside business complexity.
- Organizations that build sustained resilience continuously update recovery runbooks after every test, expand automation to reduce manual intervention, and conduct periodic architectural reviews to address new risks, integrations, and scale requirements.
- Over time, this discipline reduces recovery effort, shortens downtime, and increases confidence across both IT and business leadership.
The SAP Disaster Recovery Maturity Model
Not all SAP Disaster Recovery strategies are created equal. In practice, organizations fall across a clear maturity spectrum. Understanding where you are on this curve is the first step toward building true resilience.
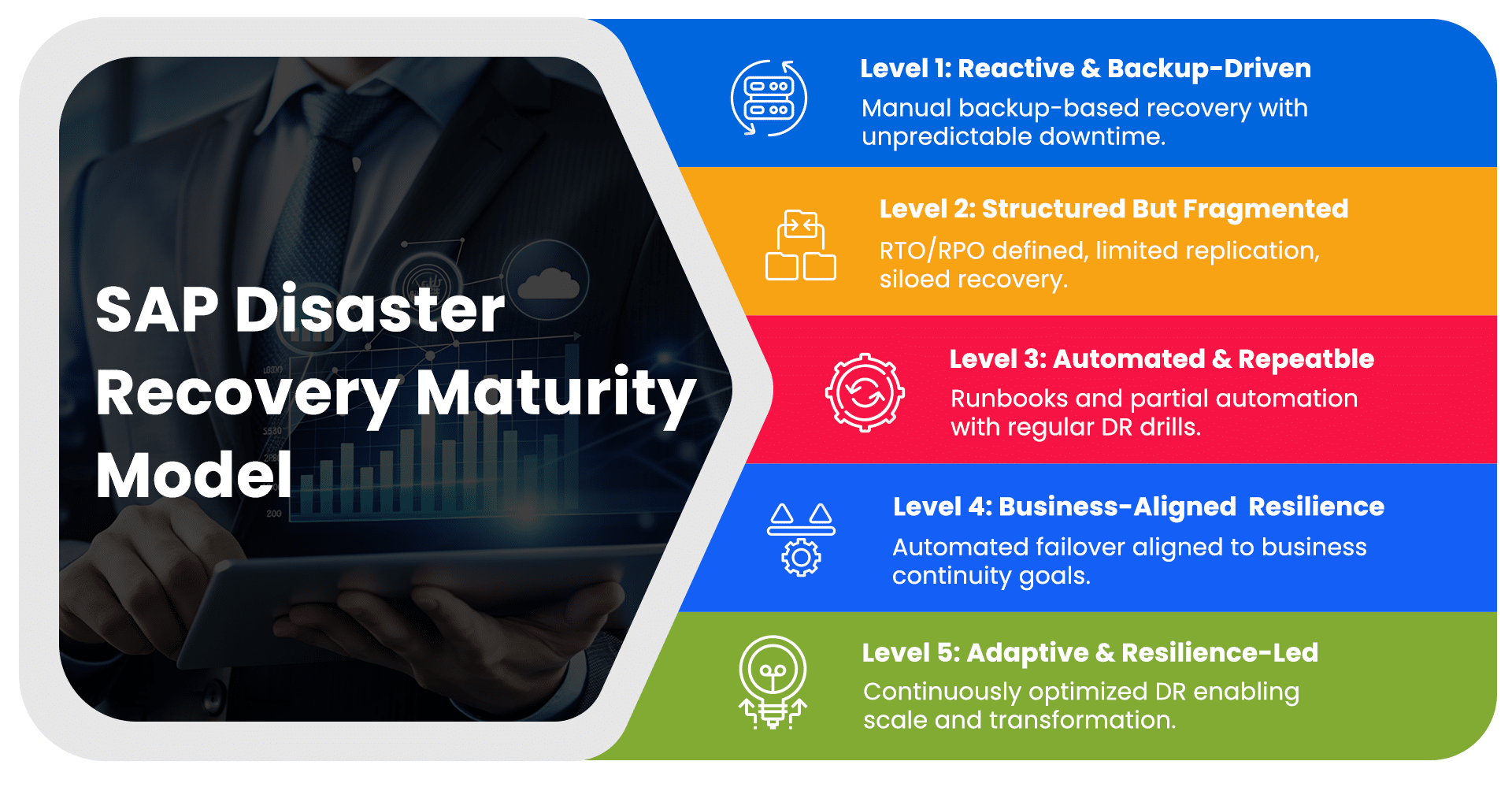
- Level 1: Reactive and Backup-Driven
Disaster Recovery relies primarily on backups with manual, untested recovery procedures. Downtime and recovery outcomes remain unpredictable. - Level 2: Structured but Fragmented
Basic RTO and RPO targets are defined, with limited replication and documentation in place. Recovery efforts are still siloed, with gaps across integrations and business coordination. - Level 3: Automated and Repeatable
Replication and failover processes are partially automated and supported by updated runbooks. DR drills are conducted regularly with measurable recovery outcomes. - Level 4: Business-Aligned Resilience
SAP DR is aligned with business continuity priorities, with automated failover and clear visibility into readiness. Cross-application dependencies are well understood and tested. - Level 5: Adaptive and Resilience-Led
Disaster Recovery is continuously optimized through automation, frequent testing, and architectural evolution. Resilience becomes a strategic enabler for scale and transformation.
Where Expertise Makes the Difference
Across complex SAP landscapes, resilience is not limited by technology. It is limited by design decisions, operational discipline, and execution maturity.
Organizations that succeed treat SAP Disaster Recovery as an engineering problem and a business transformation initiative. They design for failure, automate aggressively, test continuously, and evolve architecture as business priorities shift.
This approach requires deep SAP domain understanding, hands-on experience across cloud and on-premises environments, and the ability to translate business risk into technical outcomes.