In the rapidly evolving retail landscape, technology stands at the forefront of innovation, driving transformative solutions that redefine the shopping experience. As a result, the global retail industry is embracing rapid digital transformation in response to constantly evolving consumer demands, improving customer interfaces, and fostering innovation.
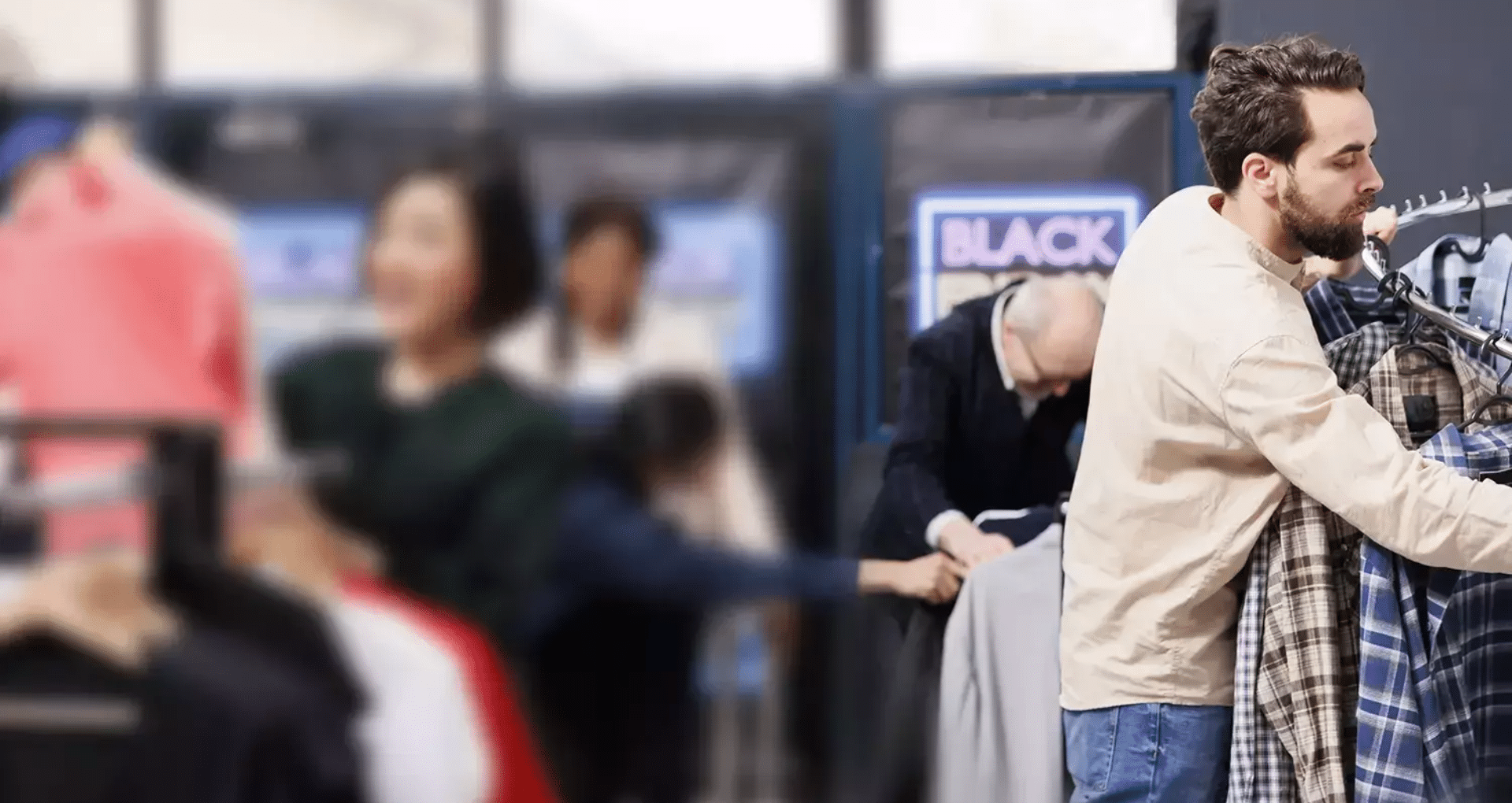
Yet, it is equally important to pay attention to a significant challenge that the retail industry is struggling to mitigate: the issue of shrinkage. The pandemic marked the beginning of retail shrinkage, and the industry has seen a downward graph since then. The average shrink rate grew to 1.6% in 2022, up from 1.4% in 2021, according to NRF’s 2023 National Retail Security Survey.
Technology offers interesting solutions to work around the pressing issue of shrinkage that is plaguing the retail industry. Let us delve into the challenge in detail and examine how modern technologies are equipped to address this effectively.
What causes retail shrinkage?
While there are multiple types of shrinkage in retail, the top reasons include operational losses, theft, shoplifting, return frauds, and employee theft, with Organized Retail Crime (ORC) topping the list. ORCs are a type of theft organized by a large-scale group backed by a criminal enterprise and accounted for a shocking 78.1% shrinkage in 2022, according to NRF’s survey. ORCs are also one of the major causes of violence in the retail industry, proving to be a risk for employees and customers alike.
It is not only the small or mid-sized outlets, but, retail shrinkage has impacted many retail giants as well. For example, Target, one of the biggest retailers in the US, has recently announced closure of nine stores, citing shrinkage as the primary reason. Many other retailers, including Dollar Tree, Home Depot, and others, have raised their concerns, citing retail shrinkage as a top concern.
How retailers can address shrinkage with technology
Digital transformation is at the forefront of retail innovation. With cutting edge technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), automation, cloud computing, and data analytics, retailers can create a more agile, efficient, and resilient supply chain that will support the demands of today’s consumers. Let’s take a closer look at how retailers can leverage these technologies:
Retail supply chain visibility is crucial for retailers to make informed, data-driven decisions. By utilizing sensors, Internet of Things (IoT) devices, and data analytics solutions, retailers can seamlessly achieve visibility. Such data-driven insights enable retailers to track inventory levels, shipments, and production processes, which ultimately helps in improving resource allocation and mitigating risks. Additionally, digital collaboration platforms help connect with suppliers, distributors, and other partners in real-time making communication, data sharing, and collaboration effortless. By embracing IoT solutions, retailers can minimize retail shrinkage while gaining more visibility, becoming more data-driven, and increasing agility. Some of the best examples include retail giants like Nike and Zara, which have implemented RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technology to maintain their inventory accuracy. RFID tags enable real-time tracking and minimize overstock and stockout situations, which are one of the reasons for shrinkage, thereby reducing retail shrinkage.
Computer vision is playing a key role in addressing shrinkage with respect to fraud or threats. This technology uses AI to recognize the posture of a buyer, correlate it with the transaction, and identify instances of “sweathearting” – instances where the customer fails to scan products or manipulates the price, thus raising real time alerts. Computer vision applications in retail use ML-based algorithms to discover consumer behavior, identify patterns, and make informed decisions on these inputs. One of the most prominent use-cases of computer vision is to detect unusual crowd movements, security breaches, and unauthorized access to enhance store safety and protect both employees and customers. Best Buy, a multinational consumer electronics retailer, uses computer vision to detect fraudulent returns. The system can identify patterns and anomalies, such as returning a large number of high-value items without a receipt or returning items different from what was purchased. The AI-powered computer vision technology marks these returns and prevents them from being processed.
Leveraging technologies to address retail shrinkage requires expertise
Leveraging technology solutions to address retail shrinkage is easier said than done. One of the most prominent hurdles to this approach is revenue leakage in retail. Revenue leakage is the potential loss of revenue due to inefficiencies, errors, and fraudulent activities within operations. Furthermore, the costs associated with implementing new technologies often become a hurdle. The initial investments in software and digital infrastructure, along with maintenance and upgrades, can potentially become a burden for smaller retailers on budget.
When it comes to implementing new technologies, integration with the existing systems becomes a critical consideration. Ensuring the compatibility of old and new technologies requires time and expertise, which can further complicate the process.
The retail industry is also one of the top industries that collects vast amounts of data, thereby making data privacy and security a critical challenge. Retailers must go above and beyond to safeguard sensitive customer data and ensure compliance to maintain trust and integrity, as it can otherwise negatively impact the customer experience.
Lastly, any digital initiative requires extensive training programs and cultural shifts for successful outcomes. Managing such transitions with the support and engagement of employees can prove to be challenging. Addressing such challenges requires a strategic approach, including meticulous planning, domain expertise, and tailored solutions that meet the business’ needs. Partnering with experts is crucial for retailers looking to leverage technology solutions to minimize retail shrinkage.
InfoVision is at the forefront of empowering retailers to navigate and overcome real-world challenges through innovative technology solutions. Our expertise spans across cutting-edge technologies such as computer vision, machine learning, and RFID, enabling us to offer a transformative approach to mitigating retail shrinkage. By integrating advanced computer vision, we elevate surveillance capabilities, while machine learning facilitates predictive analytics to foresee and mitigate potential threats. Furthermore, our use of RFID technology ensures precise inventory management, collectively forming a comprehensive strategy to fortify retailers against shrinkage. Through our retail and innovation services, we empower retailers to improve their innovation potential, flexibility, and scalability to leverage emerging technologies and sustain business growth. Our team of experts has helped many large retailers pave their way for closer brand-consumer relationships, strengthen trust, and minimize revenue leakage, thereby controlling retail shrinkage.
Embracing technology for retail revolution
Modern retailers are increasingly leveraging technology to solve their business challenges and gain a competitive advantage. In the era of instant shopping, eCommerce, and more, retailers must integrate technology solutions into their processes to gain more visibility and data-driven insights to make informed decisions and combat retail shrinkage. From inventory management to demand forecasting – the sky is the limit for technology.
To learn more about how you can leverage the power of technologies to reduce retail shrinkage, connect with us digital@infovision.com today and learn how we can help you stand differentiated and grow revenue.